Oh no, wait…Sorry, that’s a star. But you can see how I’d get confused, right?
Apparently, this is the first fuzzy photo of alien planets outside our solar system, as captured by two teams of astronomers. The pictures show four likely planets that appear as specks of white, nearly indecipherable except to the most eagle-eyed experts. All are trillions of miles away — three of them orbiting the same star, and the fourth circling a different star.
None of the four giant gaseous planets are remotely habitable or remotely like Earth. But they raise the possibility of others more hospitable.
It’s only a matter of time before “we get a dot that’s blue and Earthlike,” said astronomer Bruce Macintosh of the Lawrence Livermore National Lab, one of the photographers.
Here’s hoping.
The astronomers used a combination of ground-based telescopes and the Hubble Space Telescope to take the photos.
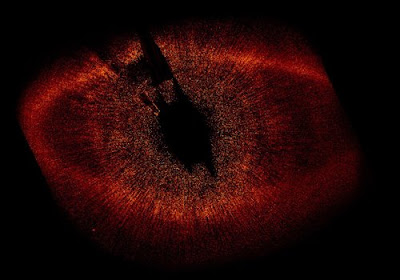
The Hubble team this spring compared a 2006 photo to one of the same body taken by Hubble in 2004. The scientists used that to show that the object orbited a star and was part of a massive red dust ring which is usually associated with planets — making it less likely to be a dwarf star.
The planet discovered by Hubble is one of the smallest exoplanets found yet. It’s somewhere between the size of Neptune and three times bigger than Jupiter. And it may have a Saturn-like ring.
It circles the star Fomalhaut (pronounced FUM-al-HUT), which is Arabic for “mouth of the fish.” It’s in the constellation Piscis Austrinus and is relatively close by — a mere 148 trillion miles away, practically a next-door neighbor by galactic standards. The planet’s temperature is around 260 degrees, but that’s cool by comparison to other exoplanets.
The planet is only about 200 million years old, a baby compared to the more than 4 billion-year-old planets in our solar system. That’s important to astronomers because they can study what Earth and planets in our solar system may have been like in their infancy, said Paul Kalas at the University of California, Berkeley. Kalas led the team using Hubble to discover Fomalhaut’s planet.
One big reason the picture looks fuzzy is that the star Fomalhaut is 100 million times brighter than its planet.
It’s a bit clearer in this photo with an inset:
– S.